Feature Highlights
- Aggregation
- Replication
- Load Balancing
- Filtering
- Packet Slicing
- GTP IP Filtering
- Timestamping
- Packet Deduplication
- Tunneling & De-tunneling
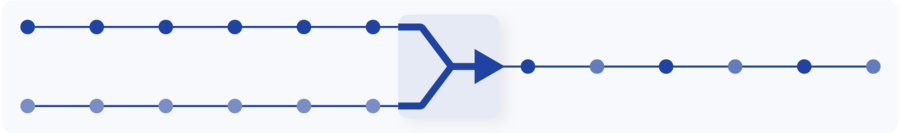
Aggregate traffic coming from multiple incoming links
Optimize port, bandwidth, and network tool utilization by consolidating traffic from multiple sources, such as Network TAPs.
Aggregation can be combined with the replication feature to send the aggregated traffic to multiple output ports. It can also be combined with both the replication and filtering features to send different parts of the aggregated traffic to different output ports.
Use case examples:
• Send traffic from multiple sources to monitoring and security tools as a single stream.
• Aggregate multiple traffic streams into higher-speed links.
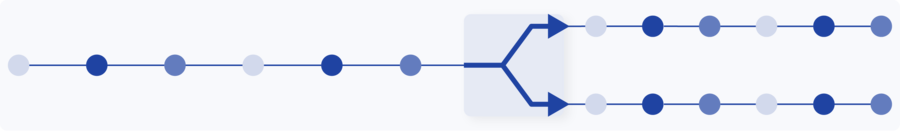
Replicate traffic to multiple monitoring and security tools
Traffic replication is the process of making multiple copies of data and forwarding them to different locations, such as NPM/APM tools, network security tools, and data storage.
Benefits of traffic replication include improving the availability of data and increasing the speed of data access.
Use case examples:
• Monitoring (tapping): send the traffic to both its intended destination and monitoring/analysis/storage systems.
• Redundancy: send the traffic to multiple network paths to avoid single points of failure and reduce the risks of downtime.
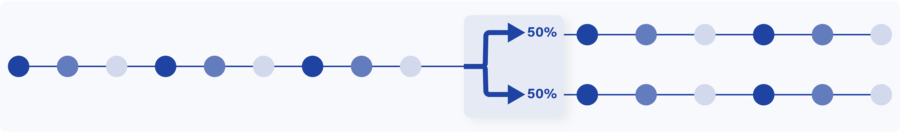
Balance traffic over multiple monitoring and security tools
When several security tools are deployed, load balancing can optimize the response time and avoid uneven load while another is idling. By distributing the traffic load evenly among the available security tools they are used in the most efficient way. A Network Packet Broker is an ideal tool for this as it sits between the TAPs and security tools.
Send only actionable data to each of the connected tools
Ensure optimum efficiency of monitoring and security tools, and bandwidth utilization, by filtering traffic such that only appropriate data is sent to these network tools.
Target specific parts of the traffic via a wide array of filter rules based on L2/L3/L4 packet headers. Filter rules support priority classes, as well as outbound options to apply to the targeted traffic.
Optimize bandwidth and storage utilization and ensure security compliance
When using packet slicing, the frame headers are kept, and the payloads dropped. By removing payloads that are irrelevant to your network monitoring and security analysis, tool overload and bandwidth usage can be decreased.
Oftentimes the tools that data is forwarded to only need information that is stored in the header of each packet. The payload does not matter. If you remove payload data from packets and leave only the header information, you ensure that only actionable data is sent across to the appropriate tool.
Another benefit of this feature is in security compliance. With packet slicing, you will be able to take out confidential data before it reaches your monitoring tools. This to ensure that this sensitive data is not being stored outside secure boundaries.
Use case examples:
• Optimizing bandwidth and storage utilization through only sending necessary data to connected tools.
• Adhere to privacy laws and security requirements by cutting out confidential data.
Filtering IP-based communication in GTP sessions
The GPRS tunneling protocol (GTP) policies contain rules that permit, deny or tunnel traffic. The Profitap X2-Series NPBs perform GTP policy filtering by checking GTP-U data-plane packets against policies that regulate GTP traffic and by then forwarding, dropping, or tunneling the packet based on these policies.
GTP is a group of IP-based communications protocols used to carry GPRS traffic within GSM and UTMS networks. It is designed as a carrier to transport actual mobile packets over the network via tunneling. The tunnel is a channel between multiple GPRS support nodes through which the hosts exchange data. All IP addresses in the GTP packets are for mobile network elements such as the base station and the serving gateway.
When IP tunneling is used to deliver IP traffic across the core network using GTP, this traffic is encapsulated. That's where the GTP IP filtering feature comes in handy. This feature will allow you to filter by IP in GTP sessions based on information in the data stream to control data flow within your infrastructure. This can be done by configuring the device to pass or drop the encapsulated traffic that doesn't match the packet policy from the mobile station through identifying the source and the destination.

Measure latency for accurate analysis
A crucial aspect of running and maintaining a network is speed. In the context of network monitoring, speed is linked to the concept of latency, referring to the speed of the network or the Remote Response time. Apart from the processing time needed on any network to process a request, there is a delay in the request to reach the network. This delay is called latency. Even though it can be challenging to improve latency, it is important to measure it with purpose-built solutions. The ability to timestamp packets with high precision is therefore essential to understanding what is going on in the network at a packet-by-packet level.
Accurate time information is important for legal and criminal investigation, and the same applies to accurate forensic analysis and performance testing to measure crucial indicators like latency.
Removes packet duplicates and provides a substantial reduction in data traffic volume
Duplicate packets are very common in networks. When accessing traffic at multiple locations in the network, picking up the same packets multiple times is almost unavoidable. When duplicate packets are transmitted to your monitoring tools, the unnecessary utilization of bandwidth and processing power reduces the efficiency and effectiveness of these tools. For that reason, detecting and eliminating identical packets is crucial, as it results in improved visibility across your network. In the X2-Series, packet deduplication is done at the interface ingress.
ERSPAN tunneling and de-tunneling, GRE de-tunneling, VXLAN de-tunneling
NGNPBs provide access to traffic encapsulated for a variety of tunneling protocols, such as Encapsulated Remote SPAN (ERSPAN), Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE), and Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN). These advanced de-tunneling features help ease blind spots of multiple traffic traversing on a network anywhere within your IT infrastructure, whether locally or remotely, physically, or virtually.
Track packets easily by adding IDs to packets based on the source (ingress) port and remove them as they leave the NGNPBs via exit (egress) ports. Using this approach, packets are encapsulated and directed from a switch/VLAN to a target IP endpoint with ERSPAN tunneling and sent to the appropriate tools. Also, by identifying and stripping the protocol, Network Engineers can selectively dictate which types of traffic should be routed to a specific device for further analysis. The X2-Series provides tunnel stripping for GRE, VXLAN, ERSPAN, IP over IP, and Teredo.
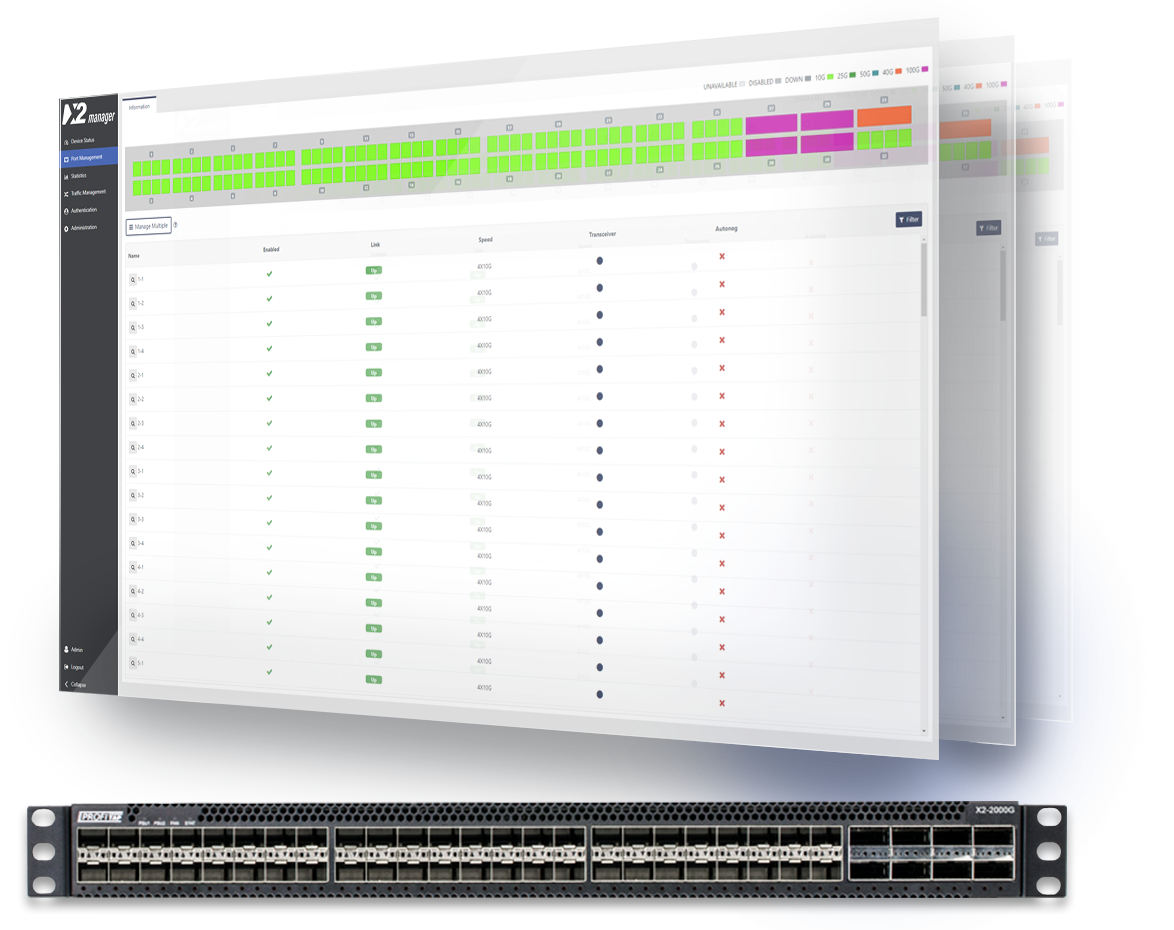
X2-Manager Overview
X2-Manager is a web-based interface that allows the user to configure and monitor the behavior of X2-Series devices. Designed with user experience and ease of use in mind, advanced configuration settings can be set and applied quickly and easily.
This web-based interface allows easy access from any OS or platform.
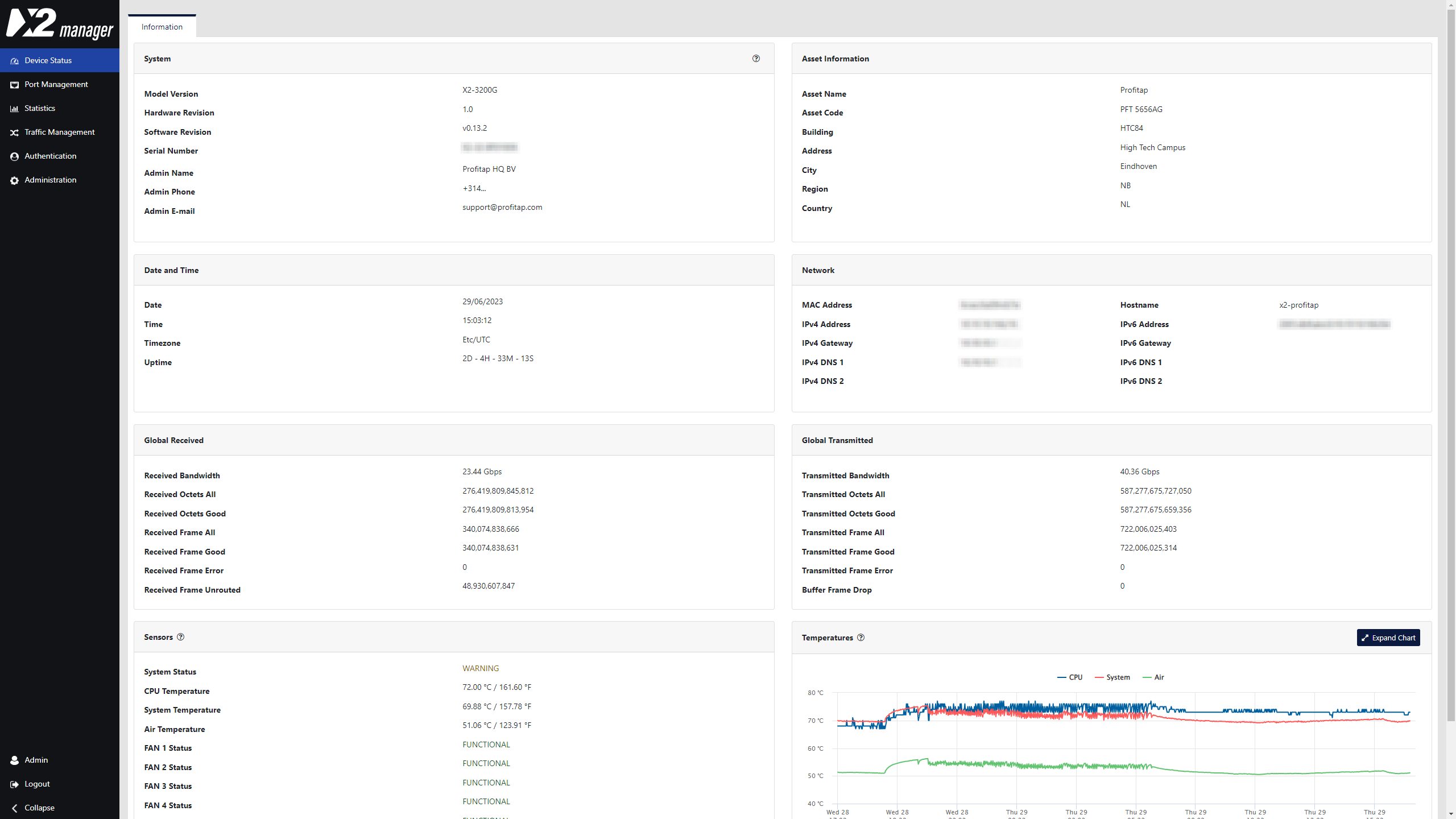
Device Status
Device status offers a quick overview of operational statistics related to the packet broker hardware. Measured temperatures are recorded with a history of 72 hours, to allow filtering back in time on temperature statistics.
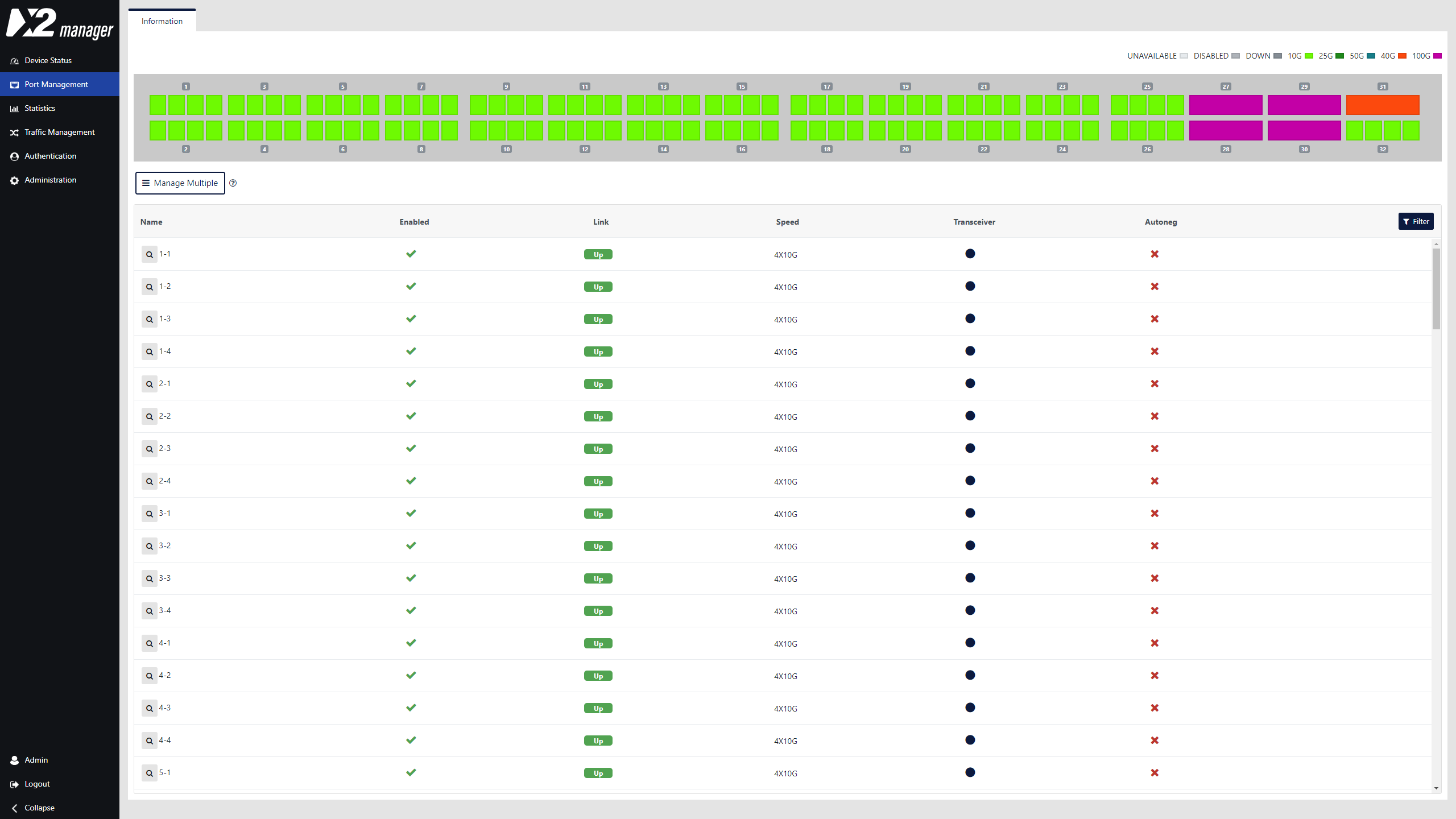
Port Management
Port management offers an instant overview of port status and speed. Users control the configuration of all QSFP modules, where each module offers additional information in the specific status section.
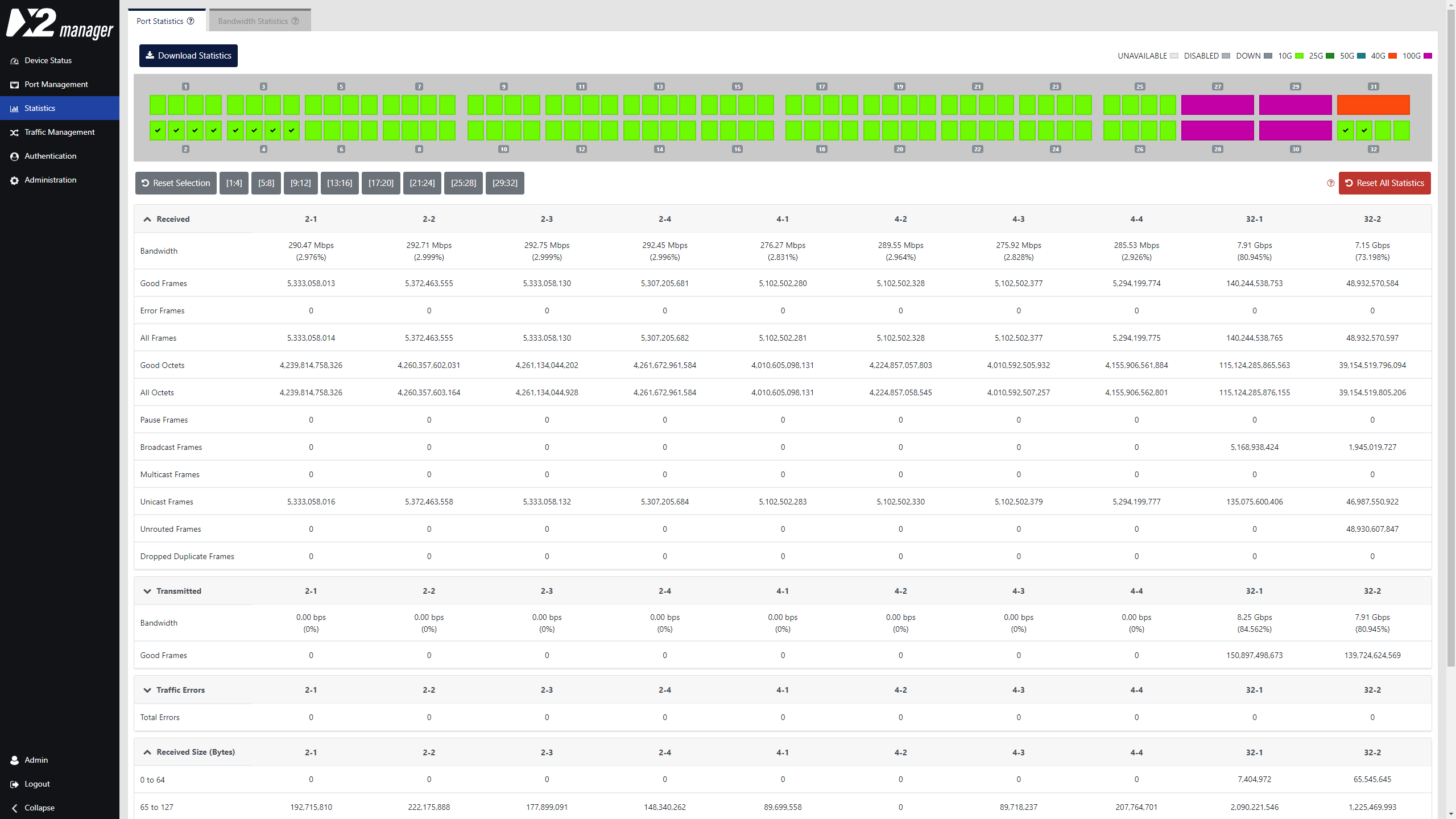
Port Statistics
Port statistics displays and monitors the statistics counter for each of the device interfaces. Users can view or export this information for a later analysis. It is also possible to easily compare the traffic bandwidth on each port.
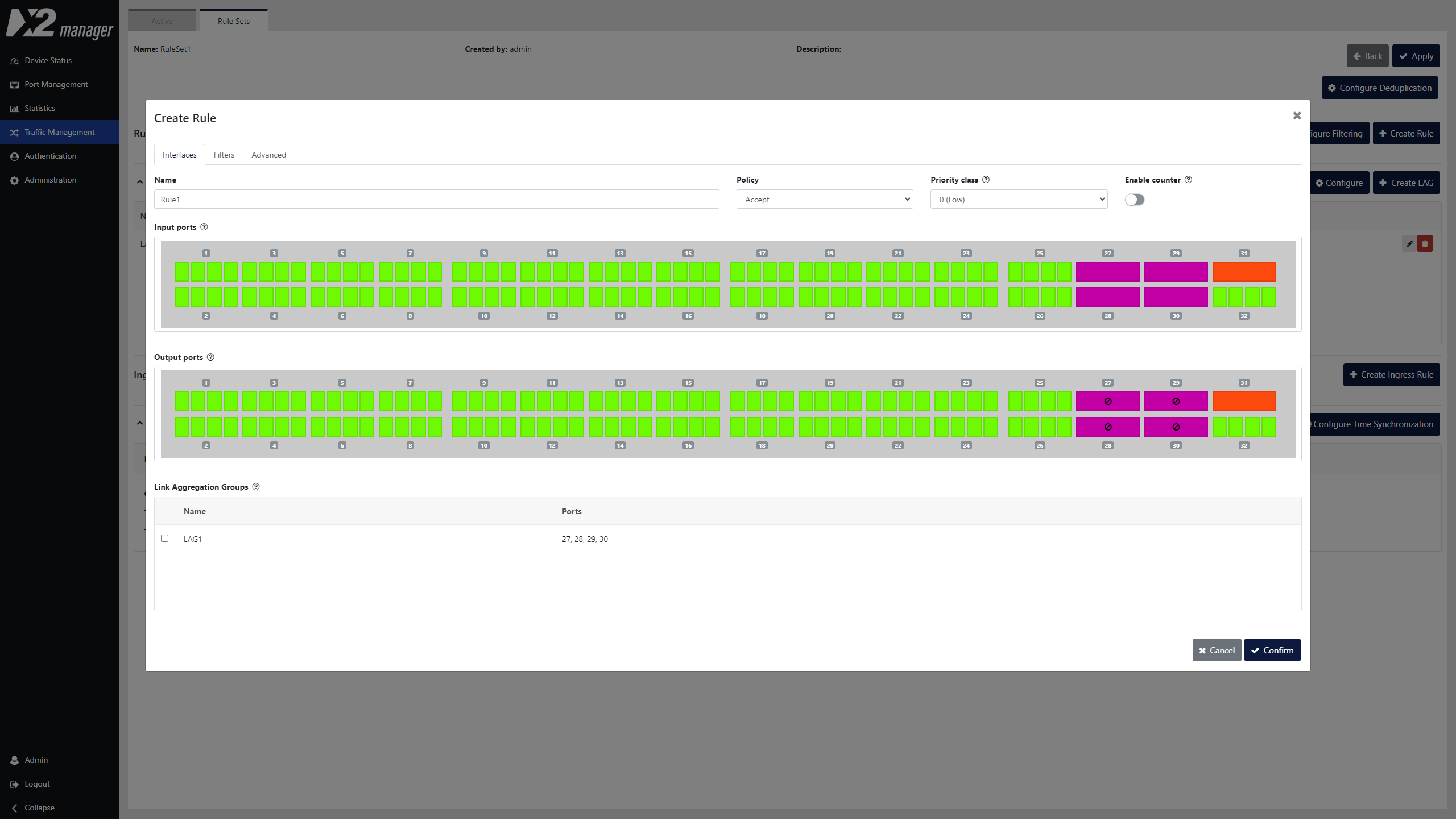
Traffic Management
Define how the traffic will flow through the device interfaces. Using a direct control interface, users are able to define aggregation, duplication, and filtering rules. Advanced actions can be defined to manipulate the traffic, adding label information, or stripping undesired headers.
-
- Aggregation, replication, filtering, VLAN tagging and stripping, MPLS stripping and load balancing (any-to-any, any-to-many, many-to-many)
- Packet slicing, timestamping, GRE de-tunneling, VXLAN de-tunneling, and ERSPAN de-tunneling
- Local and remote management (CLI, GUI, SNMP, Syslog)
- Layer 2–4 filtering
- PTPv2 time synchronization
- RESTful API support
- Flexible role-based management access
- In-line mode and in-line tool sharing
- TACACS+/RADIUS authentication
- Redundant, hot-swappable PSUs and fan modules
- Supports 1GbE, 10GbE, 25GbE, 40GbE, 100GbE
- Full control over 1GbE, 10GbE, 25GbE, 40GbE and 100GbE network traffic for monitoring thanks to its intuitive GUI.
- Multiple filter rules per port in any combination for various routing, filtering, duplication or replication and many more options can be configured by an innovative GUI to allow instant adaptation to all kinds of analysis.
- An integrated archive gives quick access to establish filter scenarios on the fly or allow instant changes to ease meeting the current requirements.
32 x 10/25G SFP28
8 x 40/100G QSFP28
8 x 10/25G SFP28
4 x 40/100G QSFP28
| PT-1G-BT-45 | PT-1G-SX-85 | PT-1G-LX-31 | PT-10G-BT-45 | PT-10G-SR-85 | PT-10G-LR-31 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 1000BASE-T SFP 100m (RJ45) | 1000BASE-SX SFP 850NM 550M (LC) | 1000BASE-LX/LH SFP 1310nm 20km (LC) | 10GBASE-T SFP+ 30M (RJ-45) | 10GBASE-SR SFP+ 850NM 300M (LC) | 10GBASE-LR SFP+ 1310NM 10KM (LC) |
| PT-25G-SR-85 | PT-40G-SR4-85 | PT-40G-LR4-31 | PT-40G-PLR4-31 | PT-40G-SR-BD | PT-40G-SR-BD-RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 25G SFP28 850nm 100m (LC) | 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ 850NM 150M (MTP/MPO) | 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ 1310NM 10KM (LC) | 40GBASE-PLR4 QSFP+ 1310nm 10km (MTP/MPO) | 40GBASE-SR-BiDi QSFP+ 150m (LC) | 40GBASE-SR-BiDi QSFP+ 150m (LC) Rx only |
| PT-100G-SR4-85 | PT-100G-LR4-31 | PT-100G-SR-BD-RX | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
|||
| 100GBASE-SR4 QSFP28 850nm 100m (MTP/MPO) | 100GBASE-LR4 QSFP28 1310nm 10km (LC) | 100GBASE-SR-BiDi QSFP28 100m (LC) Rx only |